Vaccinations
Flu vaccine
Flu vaccine is recommended to anyone 6 months and older. The Center for Disease Control predicts the virus strand each year, and create attenuated virus (dead virus) for injection. Our body’s immune system respond to these virus, and remembers them. Therefore, the next time our body is exposed to these virus, we will be ready for it.
Flu season is usually December to February in the US, CDC recommend getting the vaccine before October.
It is important that you let us know your conditions and allergies before the vaccination.
Flu vaccination is contraindicated in these populations:
- Children younger than 6 months.
- People with life-threatening or severe allergic reaction to the flu vaccine, or to any of the ingredients in the vaccine.
Flu vaccination should be used with caution in these populations:
- Patients had a severe allergic reaction to eggs who are 18 years or older can get recombinant flu vaccine, given by individuals who are experienced with managing severe allergic reactions.
- Patients had a history of mild allergic reaction to eggs (hives), can get flu shot under surveillance and safety measures.
- Patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome or a history of this disease.
- Patients who are not feeling well should discuss their symptoms with a health care provider.
For more information, please refer to the CDC website.
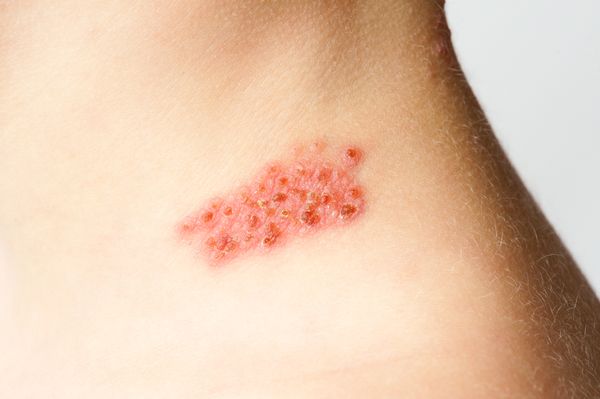
Shingrix (shingles vaccine)
Overview:
Shingles is a painful viral infection caused by varicella zoster virus, the same virus that causes chicken box. After individuals recovers from chicken pox, these virus becomes dormant. Although the exact factors that reactivate these virus is unclear, overwhelming stress and weakened immune system may lead to the resurface of the virus. Unfortunately, 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles.
Symptoms:
Initially, patient would experience tinkling or rash on either side of the body (it may also occur on the face). Then the rash becomes very painful, and they normally lasts 7 -10 days and resolves after 2 – 4 weeks. Other symptoms may include fever, chills, headache and upset stomach.
How is shingles transmitted:
Shingle is transmitted through the individual with active shingles to another individual who has never had the virus (no history of chickenpox). Individuals with active shingle presents with rash and blister. Once the blisters becomes crusty, the virus is no longer transmissible.
Complications:
Post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) is the most common complication caused by shingles virus. These are painful sites left from shingles even after patient recovers from the disease. They usually goes away after a few weeks, but they may also last for months or even years. PHN are uncommon in individuals under 40 years and younger.
Prevention:
Vaccination is the only prevent of shingles. CDC recommends those over ages of 60 to get the vaccine. The vaccination can even help to prevent further occurrence of the disease in patients who has had shingles. The vaccine can reduce the risk of shingles as well as the pain caused by the disease.
For more information, please refer to the CDC website.

Pneumonia vaccine
Pneumonia is the infection caused by Streptoccus pneumoniae. The infection can be in the blood, lungs, ear, or the tissues surrounding the brain.
Adults over 65 are at risk for pneumococcal disease.
Patients between age 19 to 64 are also at an increased risk for the disease if they have:
- Weakened immune system
- Chronic illnesses (liver, heart, lung, kidney, diabetes, asthma, alcoholism)
- Stays in long-term care facility
- Smoking
- Ear implants or Cerebrospinal fluid leaks
Types of pneumonia vaccines:
Prevnar 13® – protects against 13 strands of Streptoccus pneumoniae. It is recommended for children at age 2, 4, 6, and 12-15 months old. It is also recommended in patients over 65 years of age.
Pneumovax 23® – protects against 23 strands of Streptoccus pneumoniae. It is recommended for children 2 years and older with high disease risks, and patients 65 years and older. It is also recommended in adults age 19 – 64 with asthma or smoking.
For more information, please refer to the CDC website
